
You can achieve top fiber internet performance and reliability by optimizing your openwrt fiber router. Many homes with high-speed internet see large gaps between their fiber access speed and actual wi-fi speed. For example, households with 400-800 Mbps fiber often only get wi-fi speeds that are 340 Mbps lower than what their network can deliver. By making simple changes to your openwrt and wi-fi settings, you can close this gap and boost your internet performance. HUASIFEI brings years of network innovation to help you unlock the full potential of your fiber-optic internet and wi-fi network.
Why Optimize for Fiber?
Fiber vs. Other Connections
Fiber gives you the fastest and most reliable internet experience at home. You get high speeds because fiber-optic internet uses light to send data through glass fibers. This method keeps your connection stable and fast, even when many devices use the network at once. Other types of internet, like cable or satellite, cannot match fiber’s speed or consistency.
Here is a table that shows how fiber compares to other internet types for bandwidth and latency:
| Internet Type | Bandwidth Ranking (High to Low) | Latency Ranking (Low to High) |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber | 1. Highest bandwidth due to light-speed transmission | 1. Lowest latency, near speed of light |
| 5G Home Internet | 2. High bandwidth, sometimes competitive with fiber | 4. Lower latency than older wireless, but higher than wired |
| Cable | 3. Moderate to high bandwidth, varies with congestion | 2. Higher latency than fiber but still low |
| Fixed Wireless | 4. Variable bandwidth, generally less than cable | 3. Variable latency, generally higher than cable |
| Low Earth Orbit Satellite | 5. Varies, generally less than fixed wireless | 5. Higher latency than terrestrial but much lower than traditional satellite |
| DSL | 6. Lower bandwidth due to copper infrastructure | 6. Higher latency due to electrical signal speed limits |
| Traditional Satellite | 7. Lowest bandwidth, limited by technology | 7. Highest latency due to long signal travel distances |
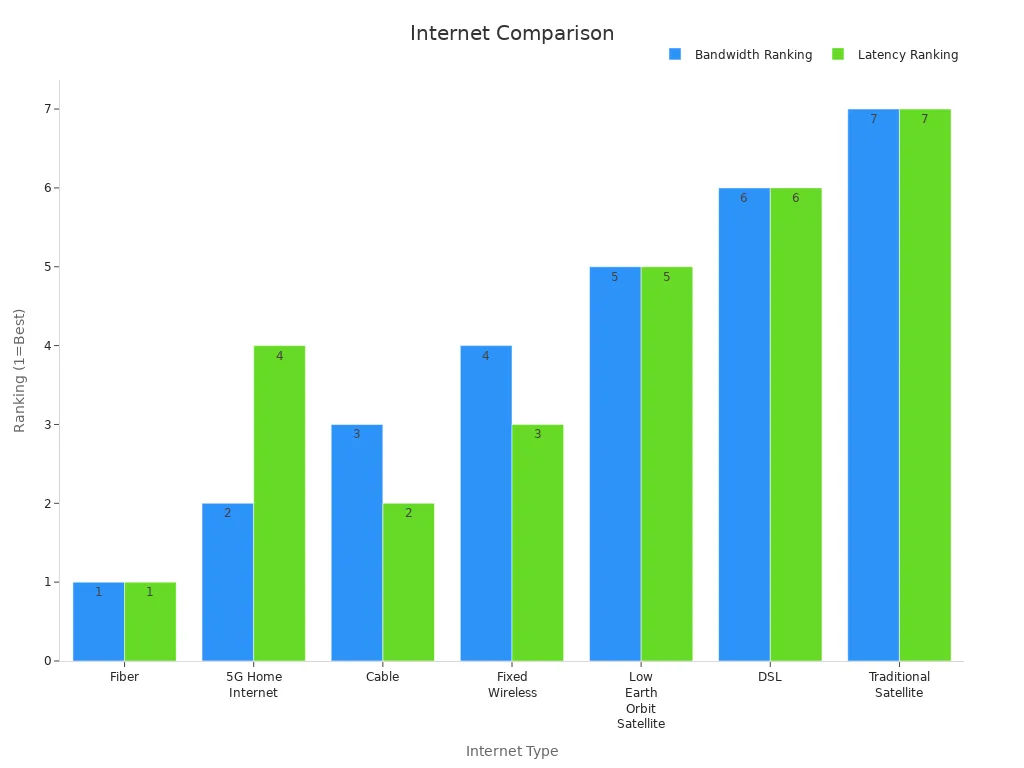
You can see that fiber-optic internet stands out with the highest bandwidth and the lowest latency. Most fiber connections deliver latency as low as 5–20 milliseconds, often under 10 ms. This means your network responds quickly, which is important for gaming, video calls, and streaming. Satellite internet, especially traditional types, has much higher latency and lower speeds. Fiber’s wired design also protects your internet from weather problems that can affect wireless links.
OpenWRT Advantages
When you use OpenWRT on your fiber router, you unlock more control and better performance for your network. OpenWRT supports hardware offloading on many modern routers. This feature lets your router handle gigabit internet speeds without overloading the CPU. For example, routers with Mediatek chipsets and mt76 drivers can manage wireless WAN traffic at up to 1 Gbit with low CPU use. OpenWRT also supports WiFi6 devices, which means your wireless network can reach higher speeds and stay efficient, even with many devices online.
You get more stable internet, faster downloads, and smoother streaming when you optimize your fiber router with OpenWRT. These advantages help you make the most of your fiber-optic internet and keep your home network running at its best.
OpenWRT Fiber Router Hardware

Fiber Compatibility
You need a router that works well with fiber to get the best internet speeds. Not all routers support fiber connections, so you should check for hardware that includes SFP ports. SFP stands for Small Form-factor Pluggable. These ports let you connect fiber cables directly to your openwrt fiber router. Many modern routers, like the Banana Pi BPI-R4 and BPI-R3, support a wide range of SFP devices. You can use RJ45, optical, or GPON ONU sticks that work with the Linux kernel and OpenWRT. For example, the Alcatel-Lucent G-010S-P and Huawei MA5671A are popular 2.5G GPON ONU SFP sticks. To use these, you need to flash them with OpenWRT firmware and set up details like your GPON Serial Number, VLAN IDs, and MAC address. This setup helps your openwrt fiber router match your ISP’s requirements and unlocks full fiber performance.
Tip: Always use genuine SFP devices for the best stability and speed with your fiber connection.
HUASIFEI Router Selection
HUASIFEI stands out as a leader in openwrt fiber router technology. Since 2012, HUASIFEI has focused on building advanced networking equipment that supports the latest fiber standards. When you choose a HUASIFEI router, you get hardware designed for high-speed fiber. Look for features like dual-core or quad-core CPUs, SFP ports, and Gigabit or 10GbE Ethernet ports. These features help your router handle fast fiber upload and download speeds. The table below shows how modern openwrt fiber router hardware supports top fiber performance:
| Feature/Statistic | Descripción/Valor |
|---|---|
| Fiber upload speeds | Up to 528 Mbps, needs high-performance routers |
| Router processors | Dual-core and quad-core CPUs |
| Ethernet ports | Gigabit and 10GbE for fast wired connections |
| Wireless technology | Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7 for strong wireless speeds |
| Advanced features | QoS, VPN, security, and firmware customization |
You can trust HUASIFEI to deliver routers that keep up with the latest fiber technology. With the right openwrt fiber router, you make sure your home network uses every bit of speed your fiber line offers.
Update OpenWRT Firmware
Firmware Upgrade Steps
Updating your OpenWRT firmware is one of the best ways to boost your router’s speed and security. New firmware versions fix bugs, patch security holes, and add new features. Many users report that running the latest OpenWRT patches on their routers leads to better stability and fewer problems. For example, older firmware like OpenWRT 19.07 is no longer supported and may have unpatched vulnerabilities. Upgrading ensures you get the latest improvements.
Siga estos pasos para upgrade your OpenWRT firmware:
- Download the correct OpenWRT firmware image for your router model from the official website.
- Log into your router’s web interface.
- Upload the new firmware file and start the upgrade process.
- Wait for the router to flash the firmware and restart.
- After reboot, install extra packages like LuCI for a user-friendly interface.
- Adjust your wireless settings, such as enabling dual-band Wi-Fi and choosing the best channel.
- Set up Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize important traffic.
- Enable network acceleration features to reduce CPU load and increase speed.
- Optimize DNS settings for faster browsing.
- Regularly check for new updates to keep your router running smoothly.
A recent upgrade can lead to a 25% increase in network efficiency and a big drop in maintenance costs. You may also see fewer network issues and better overall performance.
Keeping Your Router Secure
Keeping your router secure protects your home network from cyber threats. OpenWRT’s open-source platform gets frequent updates, which means you can quickly fix security problems. For example, the OpenWRT team recently patched a critical flaw (CVE-2024-54143) that could have allowed attackers to install malicious firmware. This fast response shows why regular updates matter.
Research shows that routers with outdated firmware often have many known vulnerabilities. Some devices run software components that are over five years old, with more than 100 security flaws. Regular firmware updates help you avoid these risks. OpenWRT also pushes fixes upstream, so your router stays ahead of threats. Commercial routers often lag behind in updates, but OpenWRT gives you a safer, faster alternative.
Tip: Always back up your configuration before upgrading. This step makes it easy to restore your settings if you need to reset your router.
By keeping your OpenWRT firmware up to date, you protect your network and enjoy the best possible fiber internet experience.
Optimising the Internet Connection
Basic Settings
You can start optimising the internet connection by adjusting a few important settings on your OpenWRT fiber router. First, set your internet speed in the router’s configuration to about 95% of your maximum fiber plan. This step helps your network handle sudden spikes in usage and keeps your connection stable. For example, if your fiber-optic internet plan offers 1000 Mbps, set the router’s speed limit to 950 Mbps. This small change can prevent congestion and packet loss.
Use high-quality Ethernet cables, such as Cat6 or Cat7, for all wired connections. These cables support the full speed of fiber and reduce interference. Poor cables can slow down your internet performance, even if you have high-speed internet. Check that all cables are firmly connected and not damaged.
Disable unused features in your router’s settings. Turn off services like USB sharing, print servers, or old wireless standards if you do not use them. This action frees up resources and improves overall performance. You can also reduce the number of devices connected to your network. Fewer devices mean less competition for bandwidth and better internet performance for each user.
Tip: Restart your router once a week. This simple habit clears memory and keeps your fiber-optic internet running smoothly.
Hardware Flow Offloading
Enabling hardware flow offloading is one of the most effective ways to boost fiber speeds on your OpenWRT router. Hardware flow offloading lets your router’s chipset handle data traffic directly, instead of relying on software. This feature is especially important for fiber-optic internet, where speeds can reach up to 1 Gbps or more.
When you turn on hardware flow offloading, you reduce the load on your router’s CPU. This change leads to faster data processing and lower latency. Research shows that routers with hardware flow offloading achieve 11 to 13 times lower execution time compared to software-only solutions. Latency drops by 76% to 86% during normal use and by 77% during heavy use. Energy consumption also falls by up to 76%. These improvements mean your network can handle more devices and higher speeds without slowing down.
| Métrica | Hardware Flow Offloading Improvement | Numerical Values |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Time | Much faster | 11×–13× lower |
| Latency (Low Intensity) | Much lower | 76%–86% lower |
| Latency (Heavy Use) | Much lower | 77% lower |
| Energy Consumption | Much lower | 72%–76% lower |
You can enable hardware flow offloading in the OpenWRT interface. Go to the firewall settings and check the box for “Software flow offloading” and “Hardware flow offloading” if your router supports it. Save and apply the changes. You will notice a big improvement in internet performance, especially when using fiber.
Note: Not all routers support hardware flow offloading. Make sure your device has this feature before enabling it.
VLAN and PPPoE
Many fiber-optic internet providers use VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) tags and PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) for authentication and traffic management. Setting these up correctly ensures you get the best internet performance from your fiber connection.
You can find your ISP’s VLAN ID and PPPoE username and password in your account details or by contacting customer support. Enter these values in your OpenWRT router’s configuration page. Assign the correct VLAN ID to the WAN interface. Set up PPPoE with your login details. This setup allows your router to communicate with the fiber network and unlocks full speeds.
If you use multiple services, such as IPTV or VoIP, you may need to set up additional VLANs. OpenWRT makes this process easy with its flexible interface. You can add new VLANs and assign them to different ports or wireless networks. This setup keeps your internet, TV, and phone services running smoothly on the same fiber line.
Callout: Always double-check your VLAN and PPPoE settings after a firmware update. Incorrect settings can cause slow speeds or loss of connection.
By following these steps, you make sure your OpenWRT fiber router delivers the highest possible internet performance. You get the most out of your fiber-optic internet and enjoy a fast, reliable network at home.
Advanced OpenWRT Features
SQM and Bufferbloat
You can unlock the full speed of your fiber-optic internet by controlling bufferbloat with smart queue management (SQM). Bufferbloat happens when your network devices hold too much data in their buffers. This causes lag and high latency, especially during heavy internet use. SQM helps you keep your internet fast and smooth by shaping traffic and reducing delays.
To enable SQM on your OpenWRT router, follow these steps:
- Go to the OpenWRT web interface (LuCI).
- Vaya a Red > SQM QoS.
- Haga clic en Enable this SQM instance.
- Enter your download and upload speeds at about 95% of your fiber plan’s maximum. For example, if your fiber-optic internet is 1000 Mbps, set download to 950 Mbps.
- Choose a queue discipline like
tartaofq_codelfor best results. - Guarde y aplique los ajustes.
Tip: You can enable packet steering in the advanced settings to improve throughput and reduce latency even more.
Real-world tests show that enabling SQM can drop upload latency from +50 ms to nearly 0 ms and download latency from +40 ms to just +9 ms during heavy use. If you want even lower latency, you can lower your download speed setting further, but most users see great results with the 95% rule. SQM is a powerful tool for gamers and anyone who needs low latency on fiber.
| Metric / Observation | Before SQM (Load Test) | After SQM (95% shaping) |
|---|---|---|
| Upload Latency | +50 ms | +0 ms |
| Download Latency | +40 ms | +9 ms |
| Target Delay | 5 ms | 5-10 ms |
| Max Throughput (with packet steering) | ~500/500 Mbps | ~500/500 Mbps |
You can see that SQM and smart queue management make a big difference in network performance. They help you get the most out of your fiber connection and keep your wi-fi running smoothly, even when many devices use the internet at once.
Calidad de servicio (QoS)
Quality of Service (QoS) lets you decide which types of internet traffic get priority on your network. You can make sure that important activities like gaming, video calls, or streaming always get the bandwidth they need. This is very useful in homes with many users or smart devices.
To set up QoS on OpenWRT:
- Ir a Network > QoS in the LuCI interface.
- Enable QoS and set your upload and download speeds just below your fiber-optic internet plan’s maximum.
- Choose a queue discipline such as
tartaofq_codelfor fairness and bufferbloat reduction. - Assign priorities to different types of traffic, such as giving gaming or video calls the highest priority.
- Save and apply your settings.
- Enabling SQM and QoS together reduces latency and ensures fair bandwidth distribution.
- QoS prevents bufferbloat by managing how much data each device can send or receive.
- You can avoid congestion and keep your network stable, even during busy times.
En main efficiency metrics for QoS include delay, delay variation, packet loss, and throughput. These settings help you control how your network handles limited bandwidth, especially at the edges where fiber meets your home devices. When you use QoS, you can stream 4K or 8K video, play games, and run smart home devices without slowdowns.
Security Settings
You can protect your fiber network and wi-fi from unauthorized access by using advanced security settings in OpenWRT. These steps help you keep your internet safe and your data private.
Follow these steps to secure your OpenWRT router:
- Change the default admin password to a strong, unique one.
- Disable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) because it is a known security risk.
- Turn off uPNP (Universal Plug and Play) to prevent unwanted access from inside your network.
- Make sure remote administration is disabled so no one can control your router from outside your home.
- Use WPA3 or WPA2+AES encryption for your wi-fi. Set a long, strong password.
- Set your wi-fi channel to 36 or 100 for 5 GHz, and use 160 MHz bandwidth if your devices support it. This gives you the best wi-fi performance on fiber-optic internet.
- Choose a unique SSID (network name) that does not reveal your router brand or model.
- Update your router firmware regularly to patch any security issues.
Note: OpenWRT routers support VPN Policy-Based Routing (PBR). You can route sensitive data through a VPN for extra security while letting other traffic use your regular fiber connection.
OpenWRT’s open-source nature lets you customize your network acceleration and security. You can add features like AI-driven threat detection, VLANs for device isolation, and advanced firewall rules. These tools help you keep your fiber-optic internet fast and secure.
| Característica / Métrica | Measurable Improvement | Impact / Benefit Description |
|---|---|---|
| Funciones de seguridad avanzadas | AI-driven threat detection without throughput loss | Keeps high network performance while blocking threats. |
| QoS and VLAN Support | Prioritizes and isolates traffic for hundreds of devices | Ensures smooth operation for smart homes and IoT devices on fiber. |
| WiFi 7 (802.11be) Support | Up to 46 Gbps wireless throughput | Supports 8K streaming, VR gaming, and real-time workloads with low latency. |
| Multi-gigabit WAN Port | 10GBase-T WAN port for fiber broadband | Handles multi-gigabit upstream connections for high-demand fiber users. |
You can see that OpenWRT’s advanced features give you control over your network’s performance and security. You get the best possible experience from your fiber-optic internet, whether you stream, game, or manage a smart home.
Wi-Fi Optimization for Fiber-Optic Internet

Channel and Band Selection
You can boost your fiber-optic internet by choosing the right wi-fi channel and band. Many homes use the 2.4 GHz band, which leads to heavy overlap and interference. This interference can slow your wi-fi and reduce the speed you get from your fiber connection. The 5 GHz and 6 GHz bands offer more channels and less interference. These bands support higher data rates and work better in busy neighborhoods.
Here is a table that shows how channel interference affects different wi-fi bands:
| Wi-Fi Band | Typical Interference | Data Rate Drop (Dense Networks) | Rendimiento |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2,4 GHz | Alta | 20-30% | Baja |
| 5 GHz | Medio | 10-15% | Más alto |
| 6 GHz | Bajo | 5-10% | Highest |
You should select channels 36 or 100 on the 5 GHz band for your wi-fi. If your router supports 6 GHz, use it for the best fiber-optic internet performance. Antenna directionality and beamforming can also cut interference by about 40% in crowded areas. By optimizing wi-fi network settings, you get faster speeds and more stable connections.
Transmit Power
Setting the right transmit power helps your wi-fi cover your home without causing problems. If you set the power too high, your wi-fi may interfere with your neighbors’ networks. If you set it too low, you may have dead spots. Start with the default setting and test your fiber-optic internet speed in different rooms. Adjust the power up or down as needed. Many routers let you change this in the wireless settings. You want strong coverage but not too much overlap with other networks.
Guest Networks
You can keep your main network safe and manage bandwidth by setting up a guest network on your fiber-optic internet router. Guest networks use VLANs or separate SSIDs to keep guest traffic away from your main devices. This protects your smart TVs, computers, and other sensitive equipment. You can set limits on bandwidth or time for guests, which stops misuse and keeps your fiber-optic internet running smoothly.
- Guest networks use passwords and encryption (WPA2 or WPA3) to keep connections secure.
- You can monitor guest traffic and update firmware to spot problems early.
- Prioritizing your main network traffic ensures your fiber-optic internet stays fast for your family.
Setting up a guest network with a different password and temporary access helps you control who uses your wi-fi. This keeps your fiber-optic internet private and reliable.
Testing and Monitoring
Speed and Latency Tools
You need to test your fiber internet regularly to make sure you get the best speed and low latency. Many tools help you measure how well your network performs. These tools give you numbers you can trust, so you know if your internet is working as it should.
ping: Checks how long it takes for data to travel to another device and back. This shows your network’s latency.traceroute: Shows each step your data takes across the internet and measures delay at each point.
Network Performance Monitoring Tools
- Obkio: Tracks your network’s latency in real time. It breaks down delays into different types, like processing or queueing.
Network Analyzers
- Wireshark and similar tools let you see every packet on your network. You can spot problems that slow down your fiber internet.
- Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR): Finds faults in fiber cables and measures their length.
- Visual Fault Locator (VFL): Helps you see breaks or bends in your fiber.
- Optical Power Meter: Checks if your fiber signal is strong enough for fast internet.
You can also use Flent, netperf, iperf3, and fast.com to test speed and latency under heavy load. These tools help you see how your network handles streaming, gaming, and downloads at the same time. When you enable Gestión inteligente de colas (SQM) on your OpenWRT router, you keep latency low even when your internet is busy. This means smooth video calls and fast gaming.
Tip: Run these tests at different times of day to spot slowdowns or spikes in latency.
Network Health Checks
You should check your network’s health often to keep your fiber internet running at top speed. Healthy networks show strong uptime, low error rates, and steady performance. Use the table below to track key statistics:
| Network Health Statistic | What It Means | Healthy Range |
|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth Utilization | How much of your internet you use | Under 60% is safe |
| Error Rate | Data sent with mistakes | Less than 0.001% is normal |
| Network Availability & Uptime | How often your network stays online | 99% or higher is good |
| Latency & Round-Trip Time | Delay for data to travel and return | Under 50ms is best |
| Jitter | Changes in delay between packets | Less than 30ms is ideal |
| Pérdida de paquetes | Data lost during transfer | Less than 1% is recommended |
If you see bandwidth use above 80% or rising error rates, your network may slow down. High latency or jitter can hurt video calls and gaming. Packet loss above 1% means your internet may drop data, causing buffering or slow downloads. By watching these numbers, you can fix problems before they affect your fiber internet.
Note: Keeping your network healthy helps you enjoy fast speeds and reliable connections every day.
Troubleshooting Fiber Issues
Slow Speeds
When you notice your fiber internet running slower than expected, start troubleshooting by checking your connection speed. Use tools like Speedtest.net or DSLReports to measure both upload and download speeds. These tests help you see if your internet matches your fiber plan. If you see a big drop, you may have a problem with your network setup or hardware.
Next, look at latency and lag during heavy use. High latency can make your internet feel slow, especially when streaming or gaming. You can use Flent or M-Labs to test how your network handles data when busy. These tools show if bufferbloat is causing delays. Bufferbloat happens when your router holds too much data, leading to lag. OpenWRT routers let you fix this by enabling smart queue management, like fq_codel or cake. After making changes, run the tests again. Compare latency and bandwidth before and after to see if your troubleshooting steps worked.
Tip: Always test your internet at different times of day. Network congestion can change your results.
ISP and Hardware Problems
If troubleshooting does not fix your fiber internet, check for issues with your ISP or hardware. Start by looking at your modem and router lights. Blinking or red lights often mean a problem with the fiber signal. Make sure all cables are secure and undamaged. Use high-quality Ethernet cables to avoid speed loss.
Contact your ISP if you see no improvement. Ask if there are outages or maintenance in your area. Your ISP can also check your fiber line for faults. Sometimes, the problem comes from the ONT (Optical Network Terminal) or SFP module. Try restarting your devices or swapping cables to rule out hardware issues.
You can track improvements by watching key metrics:
- Latency during data transfers
- Upload and download speeds
- Error rates and packet loss
A healthy fiber internet connection shows low latency, high speeds, and very few errors. Regular troubleshooting keeps your network fast and reliable.
You can unlock the full power of fiber by following these steps. Choose hardware that supports fiber-optic internet and update your OpenWRT firmware often. Enable advanced features like SQM and QoS to boost performance. Test your fiber connection and monitor network health to keep performance high. HUASIFEI gives you reliable solutions for fiber and helps you get the most from your fiber-optic internet. Enjoy fast speeds and strong performance every day.
PREGUNTAS FRECUENTES
What is the best way to check if my OpenWRT router supports fiber?
You can check your router’s specifications for SFP ports or fiber compatibility. Look for details on the manufacturer’s website or in the OpenWRT hardware database. HUASIFEI routers often list fiber support clearly in their product descriptions.
¿Con qué frecuencia debo actualizar mi firmware OpenWRT?
You should check for updates every three months. New firmware versions fix bugs and improve security. Regular updates help you keep your fiber internet fast and safe.
Why does my Wi-Fi speed not match my fiber plan?
Wi-Fi speed depends on your router’s hardware, wireless band, and interference. Use 5 GHz or 6 GHz bands for higher speeds. High-quality routers like HUASIFEI’s Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 7 models help you get closer to your fiber plan’s maximum speed.
Can I use SQM and QoS at the same time?
Yes, you can enable both SQM and QoS on OpenWRT. SQM reduces bufferbloat and keeps latency low. QoS lets you prioritize important traffic. Together, they help you get smooth streaming, gaming, and video calls on your fiber connection.